

The kinematic viscosity of a fluid can be calculated from its dynamic viscosity by dividing it by the fluid's density e.g.ĬentiPoises (cP) = centiStokes (cSt) / DensityĪ rough conversion of Redwood Seconds to centistokes is given by the formula:Ĭentistokes (cSt) = 0.260t - (0.0188/t), where t is the time in Redwood SecondsĪSTM D2161 - 05e1 Standard Practice for Conversion of Kinematic Viscosity to Saybolt Universal Viscosity or to Saybolt Furol Viscosity.
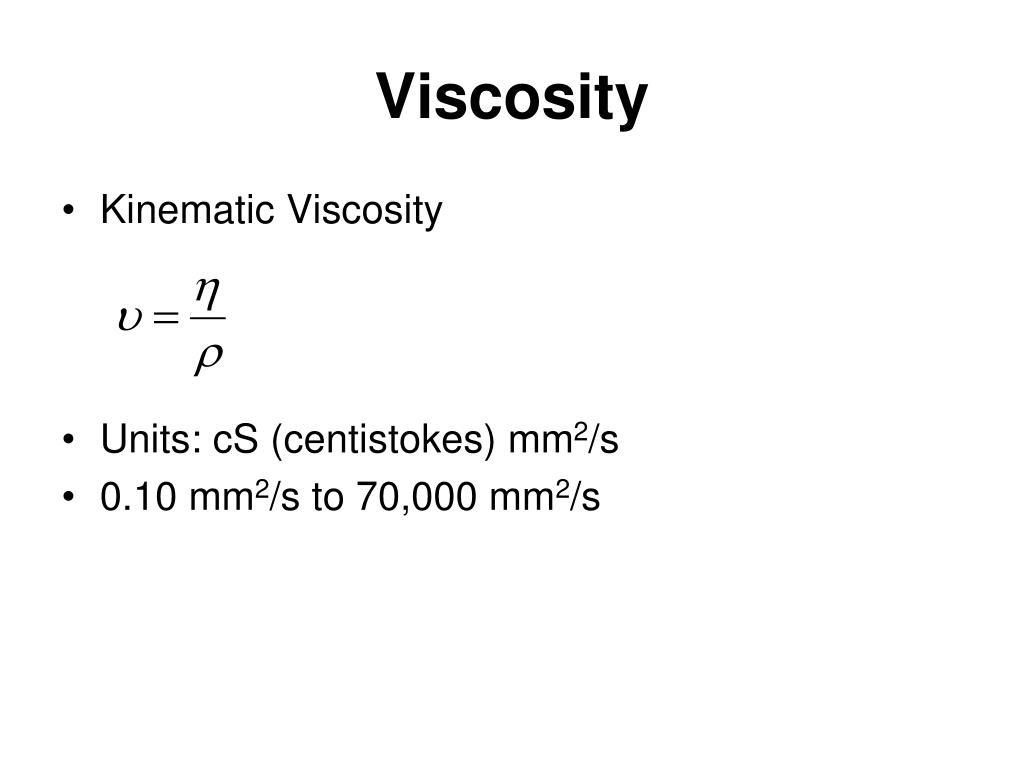
Imperial units are square foot per second. In practice the centiStoke is used since the Stoke is a large unit. The metric units of kinematic viscosity are square centimetre per second, called a Stoke (called after Irish scientist George Gabriel Stokes). Most pipe friction charts and pump correction charts used by engineers refer to kinematic viscosity. Again, the larger the molecules, the greater resistance, the higher the kinematic viscosity. Kinematic viscosity on the other hand is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow and shear under the forces of gravity. Imperial units are either slugs per foot-second, or the equivalent pound-seconds per square foot. In practice the centiPoise is used since the Poise is a large unit. The metric unit for dynamic viscosity is dyne-second per square centimetre (or sometimes the numerically equivalent gram per centimetre-second is used) called a Poise (named after French physician and physiologist Jean Louis Marie Poiseuille). The larger the molecules, the higher the internal resistance and consequently the higher the dynamic viscosity. This internal friction is caused by the resistance of the fluid's molecules moving relative to each other. The dynamic viscosity (sometimes called absolute viscosity) of a fluid can be defined as the resistance to flow and shear under the forces of internal friction. Viscosity | Definitions and Convertions Dynamic Viscosity


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
